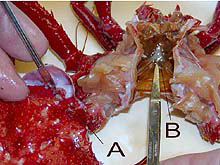
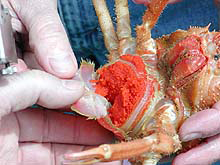
Crab ganglia. Compare the size of the dorsal ganglion (A) with that of the ventral ganglion (B) from a scarlet king crab, Lithodes couesi. Click image for larger view.
Crab Brains
June 27, 2002
Thomas Shirley and Zac Hoyt
University of Alaska, Fairbanks
![]() Watch the submersible collect a crab sample from Murray Seamount. (mp4, 10.6 MB)
Watch the submersible collect a crab sample from Murray Seamount. (mp4, 10.6 MB)
What's more important to a crab: catching food and running from predators, or daydreaming? A brief examination of a crab's nervous system will provide a quick answer. The nervous system of a crab differs from that of vertebrates (mammals, birds, fish, etc.) in that it has a dorsal ganglion (brain) and a ventral ganglion. The two nervous centers are connected by a circumesophageal ganglion, i.e., it circles the esophagus. The dorsal brain is located between the eyes and near the anterior end. The ventral ganglion is located beneath the internal organs, between the legs. The brain is tiny, smaller than the point of a pencil, while the ventral ganglion is huge by comparison. The ventral ganglion provides nerves to each walking leg and all of their sensory organs, while the brain processes sensory input from the eyes. Challenging a crab to a chess match might be a safe bet, but don't bet on trying to catch the crab!
Big Eggs and Little Eggs
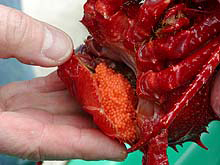
Did you know that different types of crabs have different larval life histories? Some crabs have larvae that must feed immediately after hatching, while others can spend their entire larval period (up to 5 months or more) without eating. Those larvae that must eat to grow and survive are called zooplanktivorous (they feed on zooplankton), while those having the contrasting larval strategy are called lecithotrophic (meaning they feed on energy stored in yolk). Crabs with a lecithotrophic strategy have fewer and larger eggs, while those with a zooplanktivorous strategy have many, smaller eggs. Examples of crabs with these two strategies may occur in the same habitat. For example, the scarlet king crab (Lithodes couesi) and giant spider crab (Macroregonia macrocheira) from Murray Seamount have sharply different egg sizes. The giant spider crab has a larger number of smaller eggs in comparison to the fewer, large eggs of the scarlet king crab.
Macroreg eggs. This specimen of a giant spider crab, Macroregonia macrochira, was taken from 950 m on Murray Seamount on June 27, 2002. This ovigerous female was stationary on a large rock and carrying a large clutch of relatively small diameter eggs, which is typical of a planktotrophic larval strategy. Click image for larger view.
What advantages might the two contrasting reproductive strategies have?
Crabs with lecithotrophic eggs may have the option of hatching their eggs at any time of the year, since their larvae do not have to feed. Crabs with planktotrophic larvae have large numbers of offspring to maximize the chance of dispersal and survival. Crabs with planktotrophic larvae must have seasonally pulsed reproduction to take advantage of the spring phytoplankton bloom and large amounts of food available to help insure their young's survival. The larvae of crabs with a lecithotrophic strategy are often larger and metamorphose to the benthic crab stage at a larger size, thus enhancing their survival potential. Some closely related crabs have contrasting larval strategies. For example, the red king crab has zooplanktivorous larvae, while the golden king crab has lecithotrophic larvae.
Crab Reproduction
Did you know that true crabs (brachyuran crabs, those with four pairs of walking legs) may have complex sexual strategies? Often males are attracted to females before the females molt (but some females seek out males) and remain with the females until they molt. This premating embrace is called “hand-holding.” At the time of female molting, mating occurs. True crabs have internal fertilization. The male crab transfers packets of sperm called spermatophores into paired storage organs in the female called spermathecae. The male then remains with the female until her carapace hardens.
In many species of crabs, the female may store spermatophores for several years before using them. Females are then assured that if they do not find a suitable mate, they can use stored sperm to fertilize their eggs. Also, some females cease molting when they become sexually mature, and either must store sperm or mate while hard shelled; both situations occur.
The story can be much stranger for some species. In some species of crabs, the females can mate before they become sexually mature, storing sperm until they develop gonads a year later. This sounds like every parent's nightmare, but might make good sense for species unlikely to encounter mates!
Sign up for the Ocean Explorer E-mail Update List.