
by Dr. Martha Nizinski, NOAA Fisheries National Systematics Laboratory

Dr. Martha Nizinski (right) and Dr. Anna Metaxas shared chief scientist duties during previous transboundary cruises. Here, each attends to samples collected by the Canadian remotely operated vehicle ROPOS. These samples serve as taxonomic vouchers that further our understanding of the composition, distribution, and larval transport of species among canyons. Image courtesy of Northern Neighbors: Transboundary Exploration of Deepwater Communities. Download image (jpg, 10.8 MB).
We often hear the statement that “it takes a village” to describe accomplishments that may not have been realized without a little help from our friends. So too is the case for scientific exploration and discovery. No matter the ocean, country, or province, many of the fundamental questions asked by the worldwide network of marine scientists are similar. Collaborations and partnerships allow us to move forward more quickly to address our goals. All benefit when the community of stakeholders agree to share ideas, resources, and data.
Prior to an extensive program of fieldwork dedicated to deep-sea coral habitats and submarine canyons off the northeast region (2012-2015), limited deep-sea exploration and research had been conducted recently in U.S. waters of the western Atlantic. The northeast region was considered one of the best-known areas, given the long history of exploration (dating back to the Challenger expeditions in the 1800s) and commercial fishing. But as the potential increased for fisheries and exploitation of other resources to move offshore, it became apparent that data gaps needed to be addressed.
Several management and conservation initiatives were also underway in the region and resource managers required contemporary data to better inform their decisions. Submarine canyons and deep-sea coral habitats were identified as research priorities by a variety of stakeholders. With the help of technologically advanced sampling gear (towed-camera systems and remotely operated vehicles), we quickly learned that organisms, such as deep-sea corals and sponges, were more diverse, abundant, and widely dispersed than was previously thought.
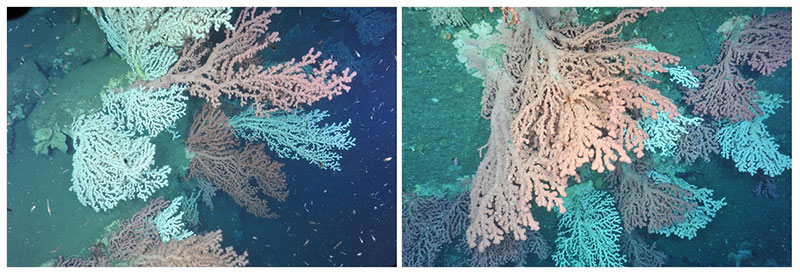
Beautiful coral gardens, dominated by the bubblegum coral Paragorgia arborea, were observed in Heezen Canyon (left) in U.S waters and Corsair Canyon on the Canadian side of the border. Large aggregations, especially of such large-sized (greater than one meter) colonies, of bubblegum coral in both canyons were amazing findings of this earlier (2014) expedition. Observations such as these contribute to our understanding of distributions and abundances of species, and also provide clues to the level of population connectivity of organisms among canyons. Image courtesy of the 2014 Bigelow-ROPOS US-Canada Gulf of Maine Collaboration. Download image (jpg, 540 KB).
Living marine resources have no geopolitical boundaries. It is this sentiment that brought together U.S. and Canadian research teams, led by Martha Nizinski and Anna Metaxas, respectively, in 2011. Collaborative research needed to be conducted in both U.S. and Canadian waters for us to better understand the patterns we observed and the underlying processes affecting deep-sea coral and sponge habitats. Three successful missions (2014, 2017, 2019) have been conducted to date.
Our primary objective was to explore and survey deep-sea coral habitats in submarine canyons off the coast of the Northeast U.S. and Atlantic Canada, as well as several locations in the northern Gulf of Maine. Scientific teams from each side of the border were selected to enhance our ability to better understand these deep-sea communities. Video; still imagery; physical samples of a variety of invertebrates, including deep-sea corals; sediment cores; water samples; and multibeam bathymetry were all collected and shared amongst the science team.
Through our efforts, we gained a better understanding of coral diversity, abundance, and distribution; tested and ground-truthed habitat suitability models; collected samples for taxonomy, coral aging and reproduction, and connectivity analyses; refined estimates of coral recruitment and growth rates; and examined the relationship between biodiversity and ecosystem function. Additionally, we provided NOAA, the New England Fishery Management Council (NEFMC), and the Department of Fisheries and Oceans (DFO), Canada contemporary data to better inform and guide the conservation of our living marine resources. Data collected during these cruises contributed to the NEFMC’s recommendation to prohibit fishing in waters deeper than 600 meters (~1,970 feet) to conserve deep-sea coral habitat, the creation of the Northeast Canyons and Seamounts Marine National Monument, and the creation of the Corsair and Georges Canyons Conservation Area by DFO Canada. Additionally, DFO will use data collected during this year’s cruise to expand their data on coral abundance and evaluate the proposed boundaries of the Fundian Channel Area of Interest (AOI), currently under consideration to become a marine protected area.
This year’s transboundary cruise aboard the Okeanos Explorer is built upon the foundation laid by Drs. Metaxas and Nizinski and their science teams. The success of their partnership, measured in new discoveries and resulting conservation actions, to name a few, has increased our awareness that we still have much to discover and learn – even in areas thought to be well known. Discussions with an expanded team of scientists has helped identify additional data gaps and areas of interest to explore and survey in the region. Through cooperation and collaboration, we are coordinating efforts and thus will reduce the likelihood of duplicating efforts in a time where resources are limited and the need for information is high, while achieving the ultimate goal of understanding, protecting, and conserving our marine natural resources in the region.
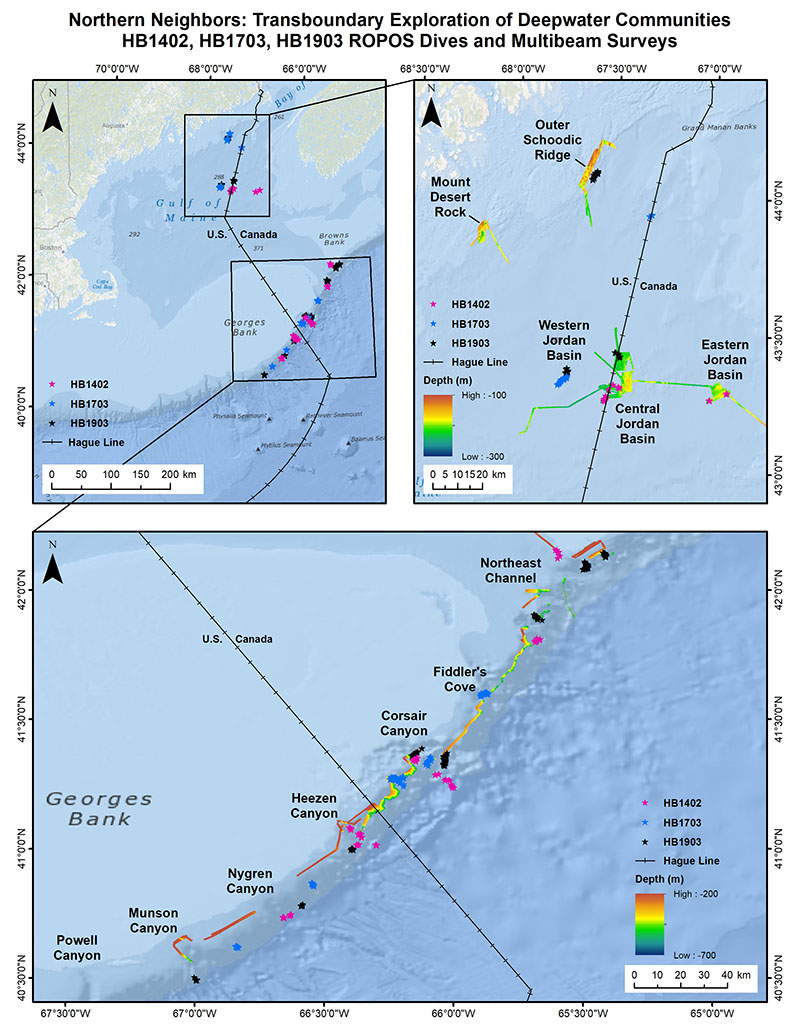
This map shows the cruise track from the 2017 transboundary cruise entitled ‘Northern Neighbors.’ Deep Connections 2019 built on earlier findings obtained during the 2014 and 2017 expeditions by filling in data gaps through expansion of the areas surveyed and by exploring poorly-known canyons on both sides of the U.S.-Canada border. Image courtesy of Northern Neighbors: Transboundary Exploration of Deepwater Communities. Download image (jpg, 3 MB).
Although we have made significant progress, more work is needed in additional underexplored canyons to the north and south of the Hague Line as well as to the east. Just as there is no hard boundary in the Atlantic between the United States and Canada, the western Atlantic is not isolated from the eastern Atlantic. Recent research initiatives in Europe and Canada have sparked a renewed interest in transatlantic cooperation. Building on the success of ACUMEN (Atlantic Canyon Undersea Mapping Expeditions), our previous transboundary collaborations fit well under the umbrella of the Atlantic Seafloor Partnership for Integrated Research and Exploration (ASPIRE) campaign.
Now is an excellent time to open up discussions with additional international colleagues and partners to tie our work more formally to the efforts underway in support of the Galway Statement on Atlantic Ocean Cooperation. Discussions with international partners have been productive. Atlantic Ocean Research Alliance (AORA), ATLAS, SponGES, Atlantic Seabed Mapping International Working Group, DFO Canada, and multiple line offices within NOAA are all on board for this expedition. Work supported in the eastern Atlantic by the European Union initiative Horizons 2020 (e.g., ATLAS, SponGES) could serve as comparison for our western Atlantic campaign. Thus, promoting forward progress toward a better understanding of the North Atlantic as a whole.
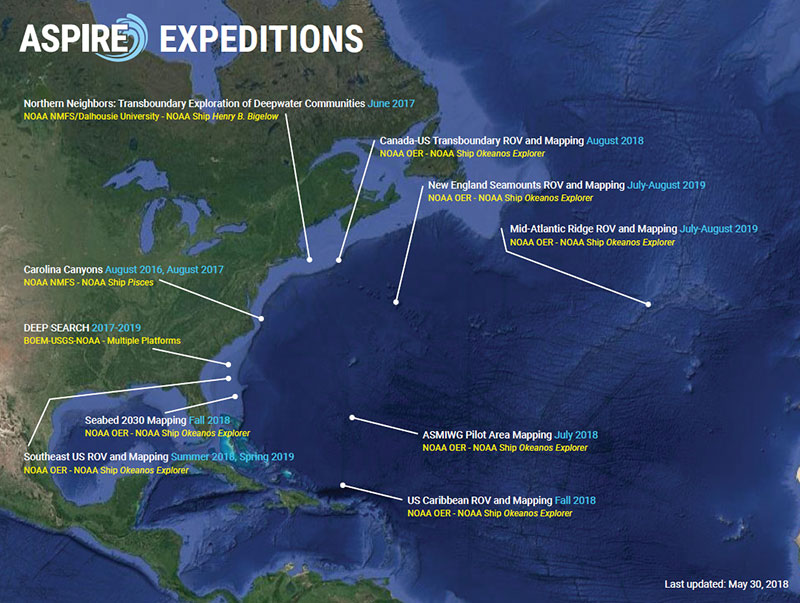
Deep Connections 2019 is the third Okeanos Explorer expedition in 2018 that will contribute to NOAA’s Atlantic Seafloor Partnership for Integrated Research and Exploration (ASPIRE) campaign, a major multi-year, multi-national ocean exploration field program focused on raising collective knowledge and understanding of the North Atlantic Ocean. This maps shows currently identified ASPIRE expeditions (2016-2019). The campaign will provide data to inform and support research planning and management decisions in the region. Image courtesy of the NOAA Office of Ocean Exploration and Research. Download image (jpg, 680 KB).
As we increase the extent of the area we will investigate and as we survey new locations, we will not only add to our knowledge and allow for better assessments of distribution and abundances of transboundary/transatlantic organisms such as deep-sea corals and associated fauna, but these data will also support the vision of AORA for “an Atlantic that is healthy, resilient, safe, productive, understood and treasured so as to promote the well-being, prosperity and security of the present and future generations.”