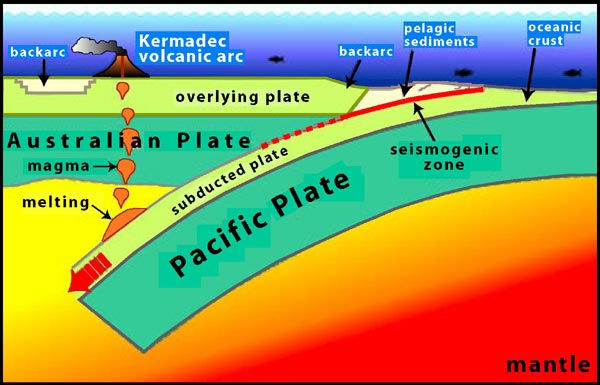
This illustration shows the Pacific plate in the east colliding with the Australian plate in the west. A consequence of this collision is subduction with the down going slab comprised of oceanic crust, or lithosphere, and a thin veneer of pelagic sediment. This causes extension behind the subduction zone, which is represented by backarc basins forming behind the arc front. At certain depths, usually around 200 kilometers (~100 nautical miles), there is melting of the subducted materials. The melting produces magmas that rise buoyantly to pond in the overlying mantle wedge and periodically erupt on Earth's surface as lavas, forming arc volcanoes. Image courtesy of Institute of Geological and Nuclear Sciences Ltd.
Related Links
New Zealand American Submarine Ring of Fire 2007
New Zealand American Submarine Ring of Fire 2007: Mission Plan