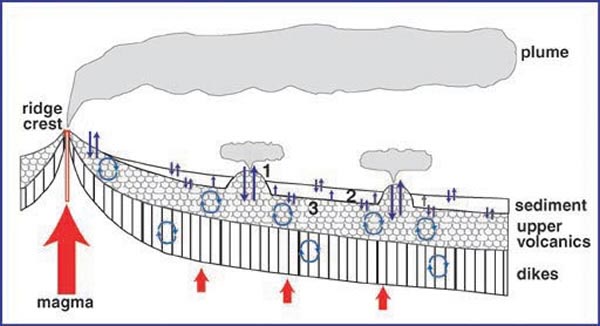
Cross-section of ocean crust, with volcanic ridge axis at left, and progressively older crust to the right. Large arrows represent flow of heat from the mantle. Small arrows represent flow of seawater and hydrothermal fluids through the crust. Primary sites of fluid exchange in older, sedimented crust may be at exposed rocky outcrops (1). There is exchange between sediment-pore fluids (2) and circulating fluids (3) within the upper, permeable volcanic layer. The deeper section of vertical dikes is much less permeable, and fluid flow is more restricted. Hydrothermal circulation continues as the crust ages, but the temperature and composition of the fluids that vent to the ocean in old crust are very poorly known. Image courtesy of Submarine Ring of Fire 2002, NOAA/OER.
Related Links
Submarine Ring of Fire 2002: Hydrothermal Vents and Ocean Chemistry